Understanding the connection between MTHFR mutations and Lyme disease could be key to managing your symptoms more effectively. Many people with Lyme disease struggle with chronic fatigue and other persistent symptoms, which can be exacerbated by MTHFR mutations. This article explores how MTHFR gene variants impact mthfr lyme disease and what this means for treatment and symptom management.
Key Takeaways
Lyme disease can cause debilitating symptoms such as chronic fatigue, and individuals with MTHFR mutations may experience intensified symptoms due to compromised detoxification processes.
MTHFR gene mutations affect folate processing and detoxification, complicating the management of Lyme disease and necessitating personalized treatment plans that address both conditions.
Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease are challenging, particularly when MTHFR mutations are involved, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach that includes genetic testing and tailored management strategies.
Understanding MTHFR and Lyme Disease
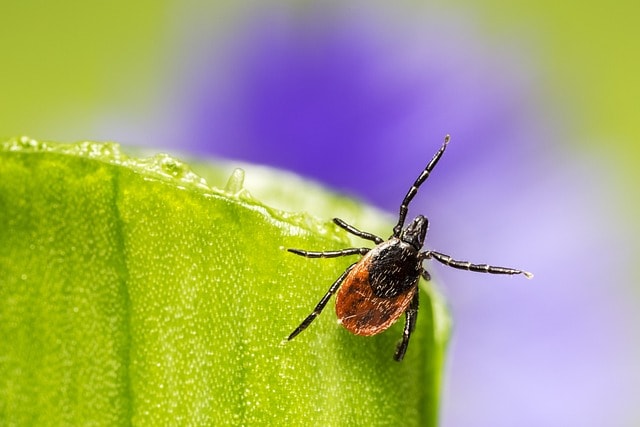

Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused primarily by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which is spread through the bites of infected ticks. This bacterial infection is prevalent in various parts of the world, including the UK, where approximately 1,500 laboratory-confirmed cases are reported annually. Including suspected cases, the total number of Lyme disease cases each year in England and Wales is estimated to be between 3,000 and 4,000.
The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary widely and often include fatigue, joint and muscle pain, and cognitive issues. Early Lyme disease symptoms may be mild and can resemble other illnesses, making it challenging to diagnose. When Lyme disease is not promptly treated, it can progress to chronic Lyme disease, a condition characterized by chronic symptoms and persistent symptoms that can severely impact a person’s quality of life.
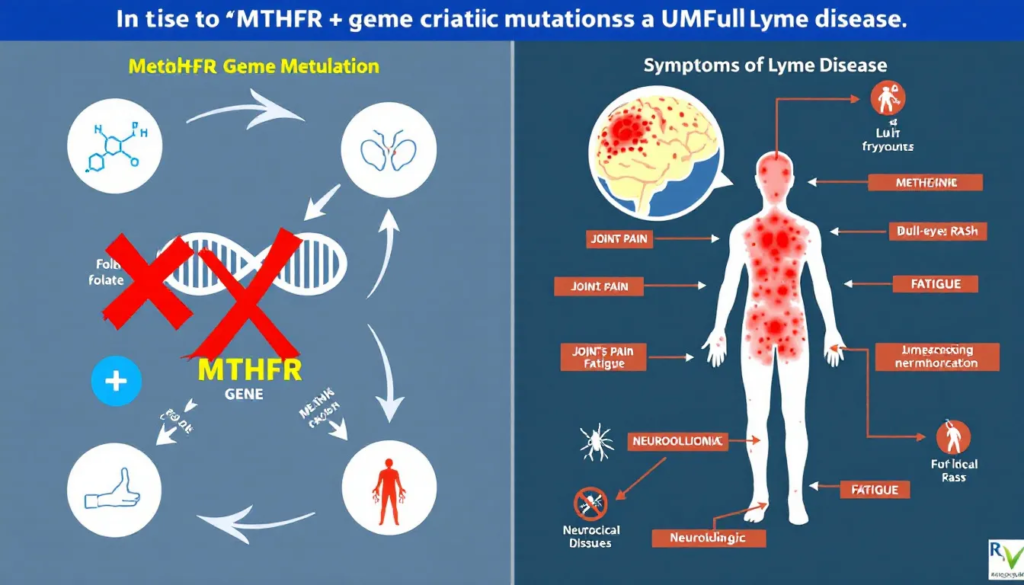
Adding another layer of complexity is the MTHFR gene, which plays a crucial role in the body’s ability to process folate and detoxify harmful substances. Mutations in this gene can interfere with these processes, leading to a range of health issues, including chronic fatigue. Understanding the interplay between Lyme disease and MTHFR mutations is essential for those experiencing persistent symptoms.
MTHFR Gene Mutations
The MTHFR gene is responsible for producing an enzyme that is vital for processing folate into its active form, which the body needs for DNA repair, methylation, and other critical functions. There are two primary variants of the MTHFR gene: C677T and A1298C. The C677T variant is often linked to cardiovascular issues due to its effect on homocysteine metabolism, while the A1298C variant is more commonly associated with chronic diseases.
Individuals with the C677T variant may struggle to convert homocysteine to methionine, leading to elevated levels of homocysteine, which is a risk factor for various health problems. On the other hand, the A1298C mutation, while not directly affecting homocysteine levels, can still disrupt other crucial processes, including inflammation control and neurotransmitter synthesis.
Defects in the methylation process caused by MTHFR mutations can have far-reaching effects on the body, making individuals more susceptible to chronic conditions and complicating the management of diseases like Lyme disease. Understanding your genetic makeup through genetic testing can be a significant step toward tailoring a more effective treatment plan.
How MTHFR Mutations Affect Lyme Disease Symptoms
Fatigue is a hallmark symptom of Lyme disease, impacting many patients’ daily lives. However, when coupled with MTHFR mutations, this debilitating fatigue can become even more debilitating. Mitochondrial dysfunction, which is often the root cause of fatigue in chronic fatigue syndrome and chronic tick-borne infections, can be exacerbated by the impaired methylation process in individuals with MTHFR mutations.
Take Allie’s story, for example. She experienced severe fatigue, generalized joint and muscle pain, migraines, digestive issues, and brain fog. These symptoms are not uncommon in Lyme disease patients, but the presence of MTHFR mutations can intensify them. After receiving treatment that addressed both her Lyme disease and MTHFR mutations, Allie’s energy levels improved, although she still faces daily challenges.
Adrenal function also becomes compromised during chronic infections, leading to increased fatigue. Researchers are working to understand how MTHFR mutations impact the response to treatments in Lyme disease patients, aiming to tailor more effective management strategies.
The Role of Detoxification in Lyme Disease
Detoxification plays a crucial role in managing Lyme disease symptoms. The body’s ability to detoxify is heavily reliant on the methylation process, which produces glutathione, a key antioxidant. The MTHFR gene is essential for producing an enzyme that converts toxins into more easily excretable forms.
However, MTHFR mutations can complicate detoxification, leading to a greater buildup of toxins in the body. This buildup can worsen Lyme disease symptoms, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and toxicity. The presence of environmental toxins and co-infections further complicates the management of chronic Lyme disease symptoms.
Effective detoxification strategies are vital for patients with MTHFR mutations. These strategies can help alleviate chronic illness symptoms by supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes. Practices such as dietary modifications, supplementation, and lifestyle changes are often necessary to enhance detoxification and improve overall health outcomes.
Diagnosis Challenges: MTHFR and Lyme Disease
Diagnosing Lyme disease, particularly in the presence of MTHFR mutations, presents several challenges. The standard two-step lyme testing method can miss a significant number of cases, especially in chronic infections. This is because conventional methods often measure the immune response rather than directly identifying the bacteria.
Many healthcare providers lack the expertise necessary to diagnose Lyme disease accurately, further complicating the treatment process. Genetic testing can identify MTHFR mutations, providing crucial information that can guide treatment strategies for improved health outcomes.
Despite treatment, many patients continue to experience persistent symptoms, suggesting that Lyme disease and its complications are not fully understood. This highlights the need for a more comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management, taking into account both Lyme disease and genetic factors like MTHFR mutations.
Treatment Strategies for MTHFR and Lyme Disease

Treating Lyme disease in individuals with MTHFR mutations requires a multifaceted approach. These patients often experience amplified symptoms, necessitating more comprehensive treatment plans. A holistic approach that includes dietary and lifestyle modifications is often essential for managing symptoms effectively.
Personalized treatment plans are crucial for effectively managing Lyme disease in patients with MTHFR mutations. These plans often involve a combination of antibiotic treatment, herbal treatments, and supportive therapies, emphasizing that recovery requires more than just medication. Incorporating activated forms of B vitamins, such as methylcobalamin, can also be beneficial.
The healing journey for many patients involves extensive lifestyle changes and therapies tailored to their unique circumstances. This can include dietary changes, such as incorporating cruciferous vegetables to enhance detoxification, and managing die-off symptoms during treatment.
Supporting the Immune System
Supporting the immune system is vital for individuals with Lyme disease and MTHFR mutations due to their compromised health status. Nutritional strategies tailored to MTHFR mutations can help improve symptoms and enhance overall health. A diet rich in plant-based foods helps reduce inflammation and supports immune function.
Regular exercise enhances blood circulation, improving the delivery of treatments and supporting detoxification. Quality sleep is essential, playing a critical role in immune health and overall recovery. Stress management techniques like meditation and yoga can alleviate symptoms associated with MTHFR mutations.
Maintaining a healthy intestinal microbiome can also be beneficial for immune regulation. Herbs such as ashwagandha may help boost adrenal function and overall immune response. Social connections and laughter are key elements in recovery, helping to mitigate the mental and physical toll of chronic illness.
Personal Stories of MTHFR and Lyme Disease

Personal stories provide valuable insights into the challenges faced by individuals with Lyme disease and MTHFR mutations. One patient experienced severe insomnia and multiple neurological symptoms before being diagnosed with Lyme and other co-infections. This diagnosis brought a sense of relief and validation for her struggles with sleep disturbance.
Another individual, after years of misdiagnosis, found hope and a renewed purpose in raising awareness about Lyme disease and its complexities. Misunderstandings surrounding Lyme disease often lead to incorrect diagnoses, such as fibromyalgia or autoimmune disorders. This means many patients may never receive adequate treatment if their symptoms are misattributed to psychosomatic conditions.
These stories highlight the importance of proper diagnosis and understanding, offering hope to those still seeking answers.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is increasingly focusing on the Multiple Systemic Infectious Disease Syndrome (MSIDS) model, which views chronic Lyme disease as influenced by numerous overlapping factors. This model emphasizes the importance of personalized treatment strategies, analyzing multiple factors affecting individual patients, including insights from infectious disease doctors.
One promising area of research is Dapsone combination therapy, which has shown potential in reducing key Lyme disease symptoms among patients who have not responded well to standard treatments. Despite the lack of consensus on chronic Lyme disease, research continues to explore possible links and develop new therapies for disease control.
Continued research and monitoring of scientific publications are crucial in advancing our understanding of Lyme disease and its interaction with MTHFR mutations, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Summary
In summary, the connection between MTHFR mutations and Lyme disease is complex but crucial in understanding chronic fatigue and other persistent symptoms. Comprehensive treatment strategies that address both conditions are essential for effective management.
Continued research and personalized approaches offer hope for improved health outcomes. By raising awareness and understanding the interplay between these factors, we can better support those living with chronic Lyme disease and MTHFR mutations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the MTHFR gene?
The MTHFR gene encodes an enzyme essential for folate metabolism and the detoxification of harmful substances in the body. Its proper functioning is vital for maintaining overall health.
How do MTHFR mutations affect Lyme disease symptoms?
MTHFR mutations can worsen Lyme disease symptoms by hindering detoxification and methylation, resulting in heightened fatigue and additional health challenges.
What are the common symptoms of Lyme disease?
Common symptoms of Lyme disease include fatigue, joint and muscle pain, cognitive issues, and in some cases, severe neurological symptoms. Early recognition and treatment are crucial for effective management.
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
Lyme disease is primarily diagnosed using a two-step testing method, although this method may overlook some cases. Genetic testing for MTHFR mutations may offer further insights into the condition.
What treatment strategies are effective for managing Lyme disease with MTHFR mutations?
An effective approach to managing Lyme disease with MTHFR mutations involves a combination of antibiotics, herbal treatments, dietary modifications, and tailored supportive therapies. This multifaceted strategy addresses both the infection and the unique challenges posed by MTHFR mutations.

